Oral pathology
Oral and maxillofacial pathology refers to diseases of the mouth, jaws and related structures. These structures include the salivary glands, temporomandibular joints, facial muscles and perioral skin (the skin around the mouth).
Oral conditions
Dr Ranchod specialises in the diagnosis and treatment of the following oral conditions:
Dental abscesses
A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus that's caused by a bacteria present in the mouth. If left untreated, the pocket of pus enlarges and may spread into the soft tissue of the face and neck. This is a potentially dangerous complication. Treatment involves drainage of the pus and treatment of the offending tooth.
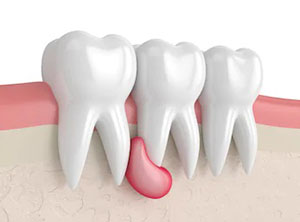
Cysts
Jaw cysts vary in size and nature. They appear as fluid-filled sacs that may only be detected by xray. Occasionally, especially when left untreated, cysts can cause facial swelling and enlargement. Cysts may become infected and cause pain.
Benign growths
A benign growth is a non-cancerous growth. Several types of non-cancerous growths can develop in the oral cavity. Very rarely, these conditions may develop into cancer. When large enough, these growths may cause facial disfigurement.
Salivary gland conditions
The most common condition of the salivary gland is a blocked duct. Blockages are usually caused by a stone or a narrowing in the duct.. Other conditions of salivary glands includes cysts, autoimmune disorders and the development of benign and malignant tumours.
Medication and radiation related jaw diseases
Certain medications (bisphosphonates) and radiotherapy are used to treat certain cancers. Unfortunately, they have side effects that can cause the jaw bone to become damaged in varying degrees.
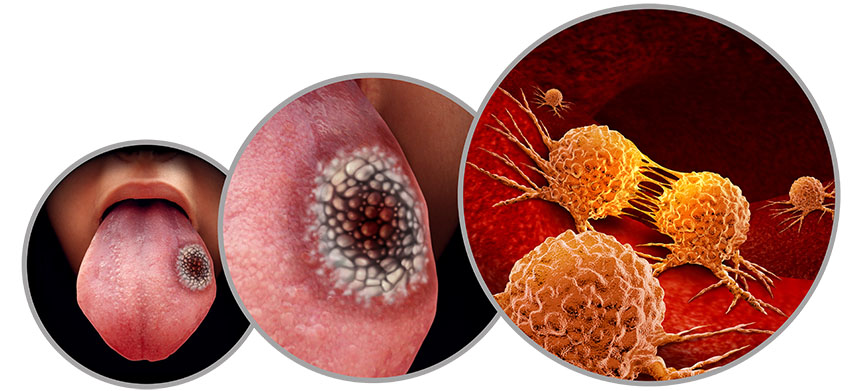
Oral Cancers
It is imperative to have a thorough examination at regular intervals to allow the early detection of oral cancer. Early detection allows the treatment to be less invasive, therefore having a positive influence on one’s quality of life.









